An invoice or bill is an important written document that indicates the sale or supply by one business to another business or consumer. It contains information about the particular sale transaction, such as buyer’s details, quantity, value, tax, and payment terms.
Many countries have laws governing the issue of invoice or bill, mostly associated with the indirect tax laws of that country. For instance, in India, the Goods and Services Tax (GST) law has elaborate laws on invoicing format and issue of invoice or bill. Let’s dive into the details of invoicing and billing.
GST, or Goods and Services Tax, is an indirect tax levied on the supply of goods and services in India. The taxation system of GST is based on the value-added tax system, wherein taxes are collected at every stage of the production process and passed on to the consumer. To keep track of the taxes collected, businesses are required to generate GST invoices and supply these to customers.
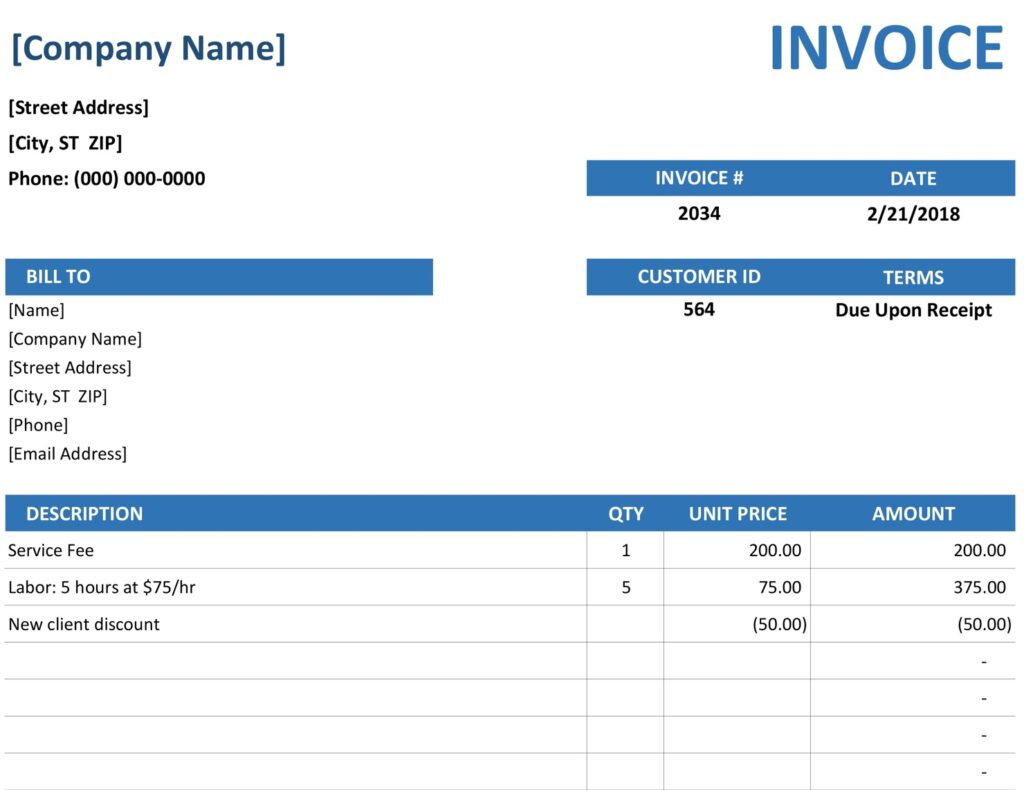
What is an invoice?
An invoice is a document that describes the goods and services that a company offers to a customer and specifies the customer’s responsibility to pay for those products and services. Invoices are the foundation of a small business’ accounting system. An invoice details how much your client owes you when payment is due and what services you rendered.
Invoices are the business records that allow companies to get paid for their services, so invoicing is critical for small businesses. Invoice can be defined as “a list of goods sent or services provided, with a statement of the sum due for these; a bill.”, as per the Oxford English Dictionary
What to remember while creating a GST invoice bill?
GST invoice is a legal document that must be issued within 30 days of the supply being made. It must contain specific details such as the GSTIN of the supplier, the GSTIN of the recipient, the date when the invoice was issued, the place of supply, and the supply details. GST invoices must also contain information about the taxes that have been applied, such as the rate of tax, the total amount payable, and the amount of GST charged. The GST invoice must also include the name and address of both the supplier and the recipient. The GST invoice must be signed and stamped by the supplier and kept as a transaction record. Businesses may also be required to issue additional documents, such as debit notes or credit notes, depending on the type of supply being made. Once you have your invoice ready with all the details included, you can print out the invoice. Make sure to keep a copy of the invoice for your records. The GST invoice should be printed on a pre-printed invoice form containing the details of the GSTIN and the business’s name. It must also include a unique serial number and the name of the supplier. In conclusion, the GST invoice format is prescribed by the government to ensure that businesses are able to keep track of the taxes they collect. Businesses must ensure that the GST invoice is issed within 30 days of the supply being made and that all details such as the GSTIN, date of invoice, and the details of the supply are included in the invoice.
Who uses an invoice, and what is the purpose?
- Invoice forms the basis for requesting clients or customers to make payments on time.
- To keep an account of the sales or supplies.
- To track the inventory of the business.
- Invoice can be used as historical data to predict future revenue.
- To keep track of business income for tax purposes.
What is an invoice due date?
In a general business context, the due date refers to the latest date by when a payment can be made on an invoice before it becomes overdue or late. These dates signify that the payment is due and will result in several penalties and interest if the payment is not received by the due date.
Since an invoice is a legal document that is part of a sale, including the due date in the invoice will keep the consumer informed. It eliminates any doubt about when the payment is due and eliminates the possibility of denying information about the payment.
FAQs
Indian laws governing invoicing?
If you have a GST registered business in India, you have to provide GST compliant invoices to your customers to sell services or goods. There is no particular format notified for an invoice. However, the invoice must have specific fields compulsorily given in Rule 46 of the CGST Rules.
Starting 1st October 2020, the country has moved from voluntary to mandatory e-invoicing requirements, being implemented in a phased manner based on turnover. e-Invoicing involves submitting an already generated standard invoice on a common e-invoice portal or invoice registration portal for validation and authentication by the GST Network.
Under GST, a tax invoice acts as evidence for supply and becomes a crucial document for the buyer or recipient to claim Input Tax Credit (ITC). It is mentioned under Section 16 of the CGST Act that the recipient should hold an invoice to claim the ITC.
Apart from GST, the Indian Customs law refers to commercial invoices for import and exports. According to current Customs procedures, an importer or exporter must send a commercial invoice and packing list along with the Customs declaration form, i.e. Bill of Entry/Shipping Bill, for both import and export.
When is an invoice raised and issued?
In general trade parlance, for the supply of goods, invoices are raised as soon as the goods are delivered with a usual credit period ranging up to 30 days from the invoice date.
When it comes to the rendering of services, invoices must be raised monthly by the end of the month. Again, a 30-day credit period is applied from the date of the invoice.
However, the time of raising tax invoices is generally determined by the GST law. There are separate time limits to issue the invoices for the supply of goods and services.
Practice area's of B K Goyal & Co LLP
Income Tax Return Filing | Income Tax Appeal | Income Tax Notice | GST Registration | GST Return Filing | FSSAI Registration | Company Registration | Company Audit | Company Annual Compliance | Income Tax Audit | Nidhi Company Registration| LLP Registration | Accounting in India | NGO Registration | NGO Audit | ESG | BRSR | Private Security Agency | Udyam Registration | Trademark Registration | Copyright Registration | Patent Registration | Import Export Code | Forensic Accounting and Fraud Detection | Section 8 Company | Foreign Company | 80G and 12A Certificate | FCRA Registration |DGGI Cases | Scrutiny Cases | Income Escapement Cases | Search & Seizure | CIT Appeal | ITAT Appeal | Auditors | Internal Audit | Financial Audit | Process Audit | IEC Code | CA Certification | Income Tax Demand Notice | Psara License | FCRA Online
Company Registration Services in major cities of India
Company Registration in Jaipur | Company Registration in Delhi | Company Registration in Pune | Company Registration in Hyderabad | Company Registration in Bangalore | Company Registration in Chennai | Company Registration in Kolkata | Company Registration in Mumbai | Company Registration in India | Company Registration in Gurgaon | Company Registration in Noida | Company Registration in lucknow
Most read resources
tnreginet |rajssp | jharsewa | picme | pmkisan | webland | bonafide certificate | rent agreement format | tax audit applicability | 7/12 online maharasthra | kerala psc registration | antyodaya saral portal | appointment letter format | GST Search Taxpayer | caro 2020 | Challan 280 | itr intimation password | internal audit applicability | preliminiary expenses | mAadhar | e shram card | aaple sarkar portal | epf activation | scrap business | brsr | depreciation on computer | west bengal land registration | traces portal | Directorate general of GST Intelligence | form 16 | rtps | patta chitta
