Copyright is a fundamental concept that protects the work of creators. It gives them exclusive control over how their creations are used, shared, and reproduced. Beyond understanding the core concept of copyright, this article will explore the significance of copyright registration. This process ensures legal protection and empowers creators to have greater control over their work. Whether you are a creator seeking to protect your content or an enthusiast interested in the legal aspects of creative expression, this article will provide valuable insights into copyright and the registration process.
Copyright registrationprocess is crucial because it establishes your legal ownership of the work. The dissemination of the work to the public, reproduction rights, and any translations or adaptations of the work are then under your control.

What Is Copyright?
Copyright is a legal entitlement granted to the owner of intellectual property. As the term implies, it pertains to the right to duplicate or reproduce a creative work. Essentially, copyright signifies that when a person produces a piece of intellectual property, they acquire ownership rights. This means that only the creator or those they authorize have the exclusive right to reproduce or utilize that work. Copyright law provides the original creators of a work with an exclusive right to utilize it or make copies for a designated period. Over time, the copyrighted work may eventually enter the public domain.
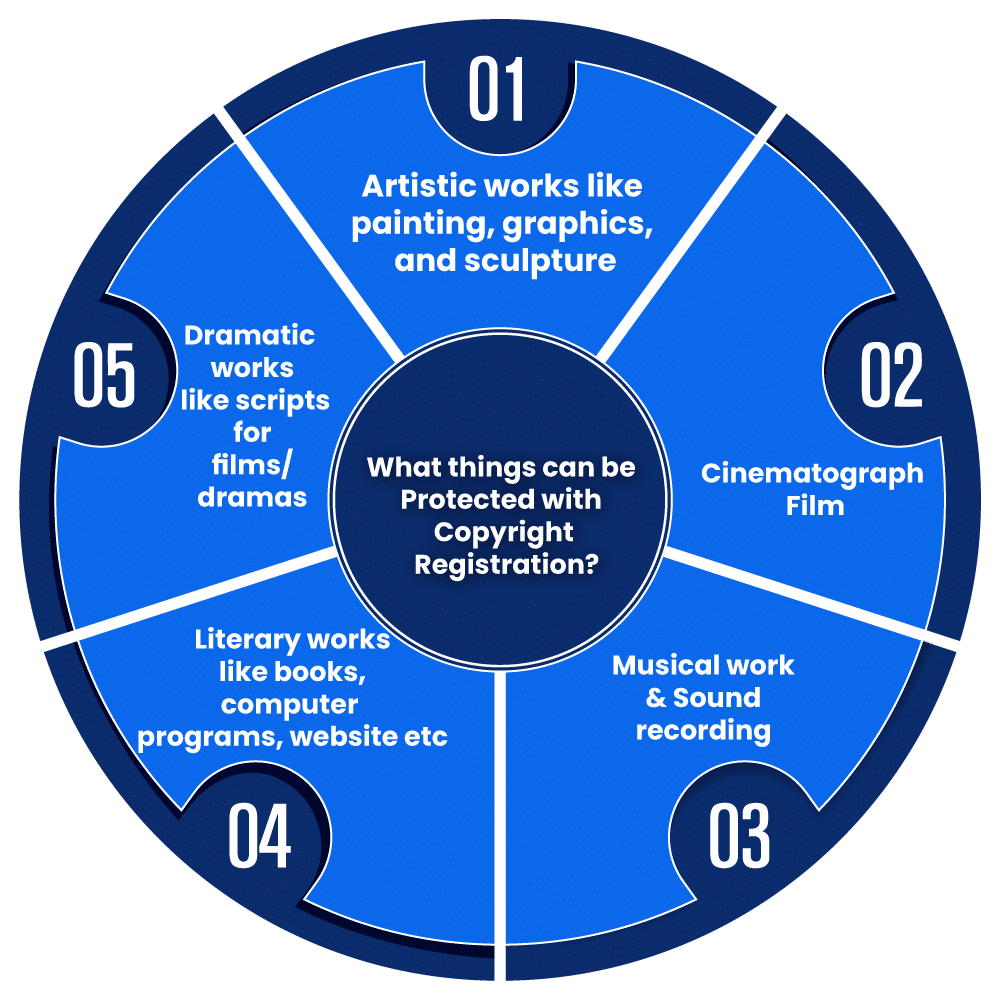
What Can You Copyright? Understanding the Categories-Copyright is a valuable tool for safeguarding a wide range of creative works. The Registrar of Copyrights maintains a comprehensive register that is divided into six distinct categories, each tailored to specific types of intellectual property:
Literary Works (Excluding Computer Programs): This category encompasses many written creations, from novels and poetry to essays, articles, and more.
Musical Works: Musical compositions, including melodies, lyrics, and sheet music, fall under this category.
Artistic Works: Visual creations such as paintings, sculptures, drawings, and other artistic expressions enjoy copyright protection.
Cinematography Films: Copyright extends to films, ensuring the protection of audiovisual works.
Sound Recordings: This category covers the audio recordings of music, speeches, and various other sound-based creations.
Computer Programs, Tables, and Compilations: Software, data compilations, and tables are safeguarded by copyright, ensuring the protection of digital innovations.
A copyright is essentially a right not to copy someone’s work. A copyright gives the owner of the subject an exclusive right over his work. If a work is protected by copyright, no one can imitate, copy or reproduce the original work in any other way. A term of copyright in India is 60 years. The register of the Registrar of Copyrights is divided into 6 categories:
1: Literary works other than computer Programs
2: Musical Works
3: Artistic Works
4: Cinematography Films
5: Sound Recording
6: Computer Programs, tables & Compilations
Copyrights are protected by “THE COPYRIGHT ACT, 1957” though there have several amendments to the act
Copyright Law
These copyrights are upheld and governed by “THE COPYRIGHT ACT, 1957,” which has undergone multiple amendments to adapt to the evolving landscape of intellectual property rights.
Why Consider Registering Your Work Under Copyright Law?
While registering your work under copyright law isn’t obligatory, it’s highly recommended for several compelling reasons. Copyright protection provides the creator with a specific set of fundamental rights over their work and assures that their creative efforts cannot be replicated for a designated period. This sense of security and legal protection fosters motivation and encourages creators to continue their artistic endeavors and produce more content.
What is the procedure to obtain a copyright registration?
To obtain the copyright registration the following process has to be followed:
- An application (including all the particulars and the statement of the particulars) in the format of FORM IV has to have to be sent to the registrar along with the requisite fees (mentioned in the Schedule 2 of the act.). A separate application has to be made for separate works
Fees for different works have been given by the government in this link: http://copyright.gov.in/frmFeeDetailsShow.aspx
- Every application has to be signed by the applicant as well as an Advocate in whose favor a Vakalatnama or a POA has been executed
- The registrar will issue a Dairy No. and then there is a mandatory waiting time for a period of 30 days for any objections to be received
- If there are no objections received within 30 days, the scrutinizer will check the application for any discrepancy and if no discrepancy is there, the registration will be done and an extract will be sent to the registrar for the entry in the Register of Copyright.
- If any objection is received, the examiner will send a letter to both the parties about the objections and will give them both a hearing.
- After the hearing, if the objections are resolved the scrutineer will scrutinize the application and approve or reject the application as the case may be.
Benefits of Copyright Registration
- Safeguarding the Owner: Copyright registration provides copyright owners exclusive rights over their work, encompassing reproduction, distribution, adaptation, dissemination, and translation.
- Legal Protection: Creators benefit from legal protection, ensuring their work cannot be reproduced without proper authorization.
- Enhancing Brand Value: A registered copyright serves as proof of ownership, allowing creators to use it for marketing purposes and contributing to goodwill creation.
- Global Reach: Copyright protection extends internationally. If a work is copyrighted in one country, it enjoys similar privileges in other countries, including India.
- Copyright as an Asset: Copyright is considered an intellectual property asset, making it an intangible resource that can be sold or licensed, adding economic value.
- Owner Visibility: Copyright registration raises the work profile, making it accessible worldwide and searchable in copyright registries. It also prevents unauthorized use of the work once registered.
- Economic Stability: Copyright registration promotes economic stability, enabling creators to reproduce and monetize their art in various forms, contributing to their financial well-being.
Legal Rights of a Copyright Owner
- Claiming Authorship: You can claim authorship of your published work, asserting your paternity over the creation.
- Reproduction and Storage: The owner can reproduce the work in any tangible form and store it in any medium through electronic means.
- Control Over Publication: You can decide where and where not to publish your work, exercising the publication right.
- Public Performance and Communication: The owner may publicly perform or communicate the work to the public. You also have the authority to create translations or adaptations of the original work.
- Protecting Reputation: In case of any potential harm to your image or reputation, you have the right to take necessary preventive actions.
- Selling or Transferring: The owner can sell or transfer the copyright, granting others the rights to use, reproduce, or adapt the work as specified in the transfer agreement.
Copyright Symbol
Once you’ve obtained copyright registration, you can use the copyright symbol (©) to indicate that your work is protected by copyright. This symbol serves as a clear notice to others that the work is under copyright protection and can help deter unauthorized use or reproduction of your creative work.
FAQs
Q: What are the rights of a copyright holder?
The copyright holder has the exclusive rights to reproduce, distribute, display, and perform the work. They also have the right to authorize others to do so.
Q: What is the duration of copyright protection in India?
The duration varies depending on the type of work. Generally, it lasts for the lifetime of the author plus 60 years. For anonymous and pseudonymous works, it is 60 years from the date of publication.
Q: What works can be copyrighted?
Copyright can be obtained for a variety of works, including literary works, artistic works, musical works, sound recordings, cinematographic films, and computer software.
Practice area's of B K Goyal & Co LLP
Income Tax Return Filing | Income Tax Appeal | Income Tax Notice | GST Registration | GST Return Filing | FSSAI Registration | Company Registration | Company Audit | Company Annual Compliance | Income Tax Audit | Nidhi Company Registration| LLP Registration | Accounting in India | NGO Registration | NGO Audit | ESG | BRSR | Private Security Agency | Udyam Registration | Trademark Registration | Copyright Registration | Patent Registration | Import Export Code | Forensic Accounting and Fraud Detection | Section 8 Company | Foreign Company | 80G and 12A Certificate | FCRA Registration |DGGI Cases | Scrutiny Cases | Income Escapement Cases | Search & Seizure | CIT Appeal | ITAT Appeal | Auditors | Internal Audit | Financial Audit | Process Audit | IEC Code | CA Certification | Income Tax Penalty Notice u/s 271(1)(c) | Income Tax Notice u/s 142(1) | Income Tax Notice u/s 144 |Income Tax Notice u/s 148 | Income Tax Demand Notice | Psara License | FCRA Online
Company Registration Services in major cities of India
Company Registration in Jaipur | Company Registration in Delhi | Company Registration in Pune | Company Registration in Hyderabad | Company Registration in Bangalore | Company Registration in Chennai | Company Registration in Kolkata | Company Registration in Mumbai | Company Registration in India | Company Registration in Gurgaon | Company Registration in Noida
